Quick Fact – Decarbonization – Part 2
Energy Generation: : This is a four-part series looking at how climate impact is rapidly changing our world and the coming challenges as we make the transition to a future that is climate sustainable.
- Shifting from fossil fuels to clean hydro, solar and wind: Washington state is a leader in decarbonizing initiatives. In 2019, Washington State passed the historic Clean Energy Transformation Act (CETA). It puts into motion a complex set of interdependent actions intended to speed a transition to clean energy and shut down coal-powered plants. CETA commits the state to a path for no coal generation by end of 2025, greenhouse gas neutral by 2030, and 100% renewable or zerocarbon resources by 2045.
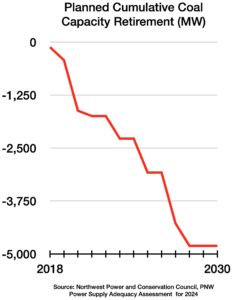 This is a bold move, though it comes at a price:
This is a bold move, though it comes at a price:
- Coal accounts for about 11% of NW energy capacity.
- Rapidly shutting down coal power plants will reduce the regional capacity to meet peak loads (see chart). Especially in cold winter months.
- Reduced capacity will increase the potential for regional power outages and rolling blackouts.
- CETA recognizes hydropower as a critical lowcarbon source of generation to replace coal, as well as firm intermittent renewables like solar and wind power
- Coal power will also be replaced with new solar and wind power, firmed by hydro and battery storage.
- But it will take years to develop new renewable energy sources to replace that coal power and cost billions of dollars. To put it into perspective, all the wind and solar power developed in the Northwest in the past 20 years is a small fraction of what will be required in the next 10 years to avoid capacity shortfalls.
Decarbonizing energy generation is just part of the strategy to reduce carbon emissions. Decarbonizing energy consumption is equally important.
Learn more:
- Read the full four part Quick Fact series at: www.opalco.com/quick-facts
- OPALCO Integrated Resource Plan
- PNW Power Supply Adequacy Assessment for 2024
- WA Clean Energy Transformation Act



